
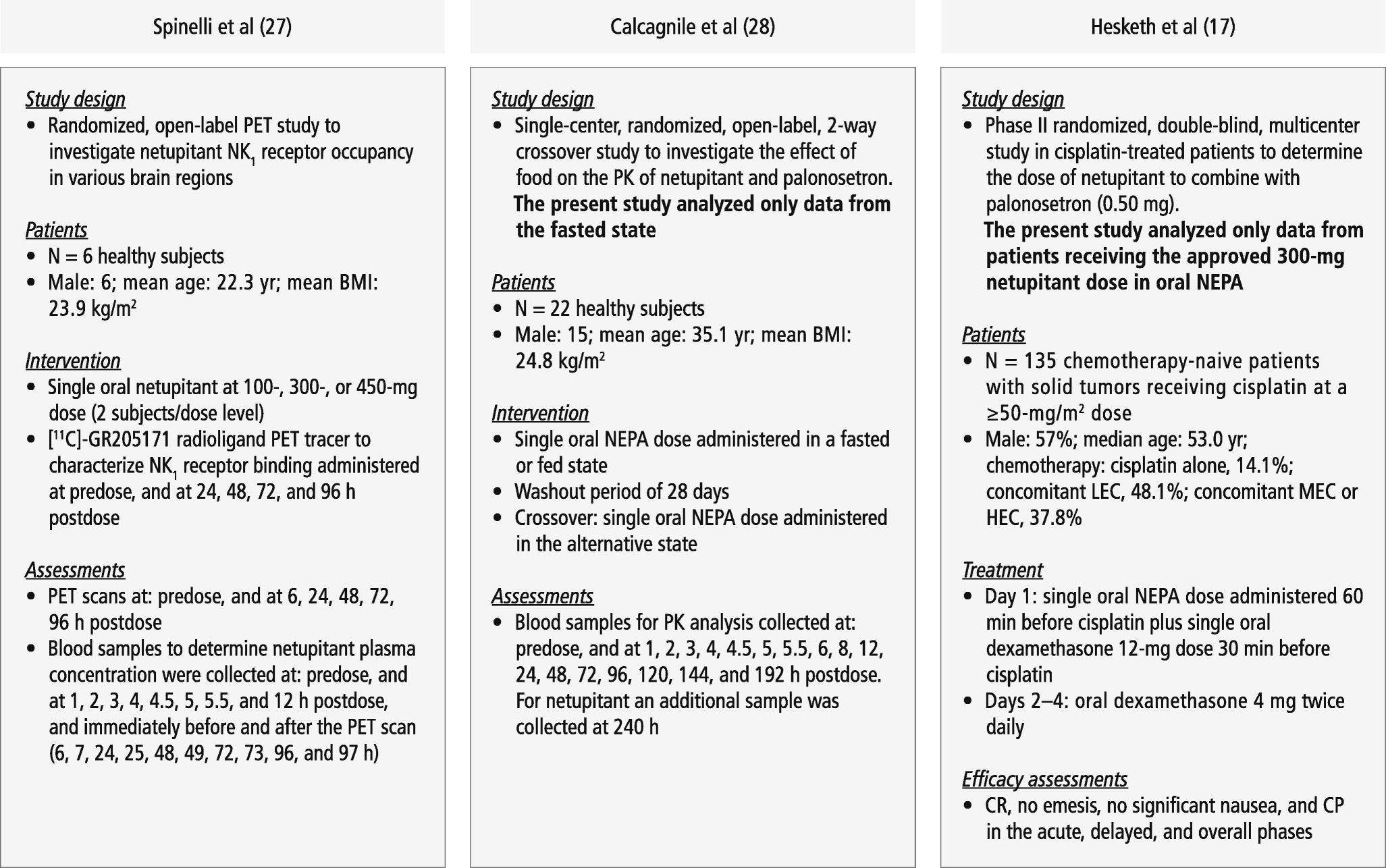
In the United States, the combinations of netupitant/palonosetron and fosnetupitant/ palonosetron (brand name Akynzeo) are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the prevention of acute and delayed chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, including highly emetogenic chemotherapy such as with cisplatin.

National Library of Medicine.Netupitant is an antiemetic medication. "Netupitant mixture with palonosetron".Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. "Netupitant PET imaging and ADME studies in humans". ^ a b Spinelli, T Calcagnile, S Giuliano, C Rossi, G Lanzarotti, C Mair, S Stevens, L Nisbet, I (2013)."In vitro and in vivo pharmacological characterization of the novel NK(1) receptor selective antagonist netupitant". ^ Rizzi A, Campi B, Camarda V, Molinari S, Cantoreggi S, Regoli D, Pietra C, Calo G (2012).Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 June 2016. ^ a b c d e f g "Akynzeo: Summary of Product Characteristics" (PDF).^ "FDA approves Akynzeo for nausea and vomiting associated with cancer chemotherapy" (Press release).Archived from the original on 18 October 2020. ^ a b "Akynzeo- netupitant and palonosetron capsule Akynzeo- fosnetupitant and palonosetron injection".Biological half-life is 88 hours, significantly longer than that of the first NK 1 receptor antagonist, aprepitant, which has a half-life of 9 to 13 hours. Netupitant and its metabolites are mainly excreted via the faeces. The main metabolites are desmethyl-netupitant (M1), netupitant N-oxide (M2), and hydroxy-netupitant (M3) all three are pharmacologically active. The substance is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4, and to a lesser extent by CYP2D6 and CYP2C9. Netupitant and its main metabolites (called M1 and M3) are bound to plasma proteins to more than 99%, and M2 protein binding is 97%. Availability is moderately (10–20%) increased when taken after a fatty meal. Highest blood plasma concentrations are reached five hours after application. Pharmacokinetics īioavailability is estimated to be over 60% for orally taken netupitant. The NK-receptor is a G-protein receptor coupled to the inositol phosphate signal-transduction pathway and is found in both the nucleus tractus solitarii and the area postrema. SP is found in neurons of vagal afferent fibers innervating the brain-stem nucleus tractus solitarii and the area postrema, which contains the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ), and may be elevated in response to chemotherapy. Netupitant competitively binds to and blocks the activity of the human substance P/NK1 receptors in the central nervous system (CNS), thereby inhibiting NK1-receptor binding of the endogenous tachykinin neuropeptide substance P (SP), which may result in the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV). Netupitant is a selective neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonist with potential antiemetic activity. Netupitant is a selective NK 1 receptor antagonist. This effect has been observed with dexamethasone, the anti-cancer drugs docetaxel and etoposide, and to a minor (not clinically significant) extent with levonorgestrel, erythromycin and midazolam. īeing a CYP3A4 inhibitor itself, netupitant could also increase plasma levels of pharmaceuticals that are metabolized by CYP3A4. Netupitant blood plasma levels are expected to increase when combined with inhibitors of the liver enzyme CYP3A4 and lowered when combined with inductors of this enzyme. Side effects of the combination netupitant/palonosetron are similar to palonosetron alone, so that no common side effects can be attributed to netupitant. In the European Union, the combinations are approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the same indication.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
